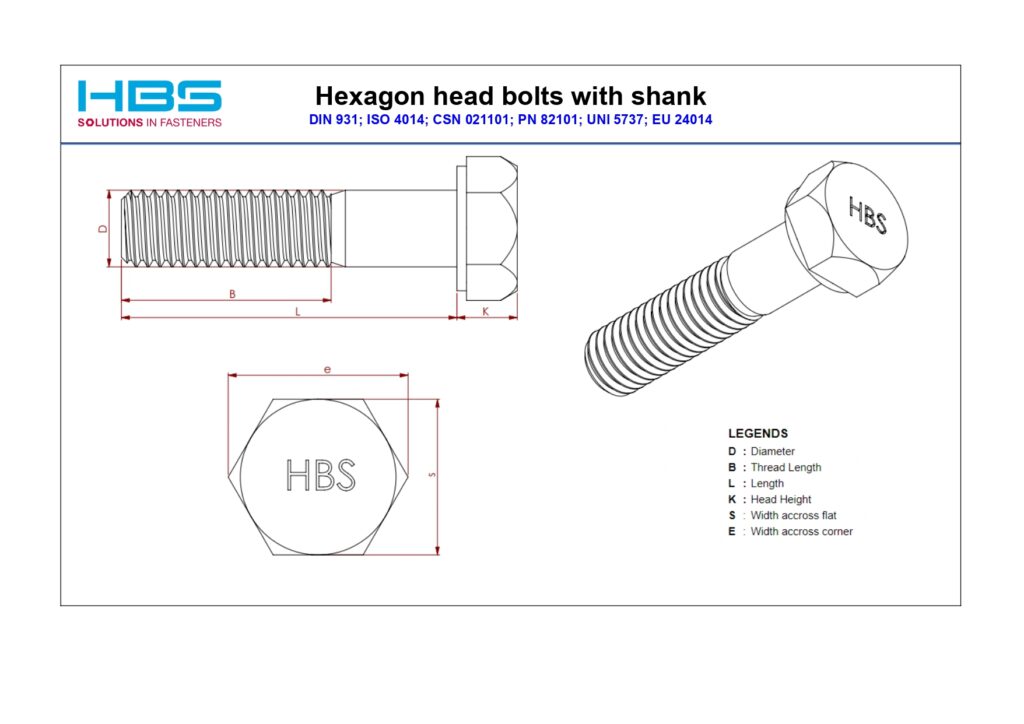
Hex Bolt : Partial Threaded
Technical Specification:
- Hex Bolt : Partial Threaded
- Din 931/ISO 4014
- Fully Threaded
- Diameter: Metric or Inch
- Length: Metric or Inch
- Thread: Coarse or Fine
Possible materials:
- ISO: 8.8., 10.9, 12.9
- ISO: A2, A4
- ANSI/ASME: A193-B7, A320-L7, A307
- ANSI/ASME: A193-B8(M) Cl.1 & Cl.2
- DIN Werkstoff: 42CrMo4, 25CrMo4
Possible coatings:
- Carbon steel: Hot-dip Galvanizing, Geomet-500, Zinc, Zinc-Nickel, PTFE/Xylan, TAKECOAT-1000
- Stainless steel: PTFE/Xylan, TAKECOAT-1000
Applications:
- Structural
- Machinery equipment
- Automotive
- Aerospace
Understanding the Uniqueness and Advantages of Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931
When it comes to securing components in various industries, the choice of fasteners plays a pivotal role. Among the diverse range of fasteners available, Hex Bolts are widely recognized for their reliability and strength. In particular, the Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 stands out for its distinctive design and application-specific advantages.
What Sets Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 Apart?
The DIN 931 specification for Hex Bolts refers to a partially threaded design. Unlike fully threaded bolts (like those adhering to the DIN 933 standard), these bolts have an unthreaded shank section. This unique feature of the DIN 931 Hex Bolt offers several key benefits:
- Enhanced Strength and Load Distribution: The unthreaded portion of the DIN 931 Hex Bolt provides a stronger grip compared to fully threaded bolts. This is because the unthreaded shank can bear the shear loads more effectively, distributing the stress over a larger area.
- Precision Alignment: The smooth shank of the DIN 931 bolt aids in precise alignment of the fastened components. This is especially crucial in applications where the alignment is critical for the assembly’s performance.
- Improved Durability: With less thread exposure, the DIN 931 Hex Bolt is less susceptible to wear and tear in high-vibration environments. This results in a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
DIN 931 vs. DIN 933: Choosing the Right Fastener
While the DIN 931 and DIN 933 Hex Bolts may appear similar at first glance, their applications are distinct due to their threading. The DIN 933 Hex Bolt is fully threaded and is typically used in applications where the bolt length needs to engage with the entire threading for secure fastening.
In contrast, the Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 is particularly advantageous in applications where the strength of the connection is paramount, such as in heavy machinery, structural applications, and automotive assemblies. Its partial threading makes it the preferred choice when shear resistance and alignment are crucial.
The Ideal Fastener for Demanding Applications
The Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 is an exceptional choice for demanding applications that require robustness, precise alignment, and durability. Its design superiority over fully threaded bolts like the DIN 933 makes it a go-to fastener for industries seeking reliability and performance.
For your fastening needs, consider the Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 for a solution that combines strength, precision, and longevity.
In contrast, the Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 is particularly advantageous in applications where the strength of the connection is paramount, such as in heavy machinery, structural applications, and automotive assemblies. Its partial threading makes it the preferred choice when shear resistance and alignment are crucial.
The Ideal Fastener for Demanding Applications
The Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 is an exceptional choice for demanding applications that require robustness, precise alignment, and durability. Its design superiority over fully threaded bolts like the DIN 933 makes it a go-to fastener for industries seeking reliability and performance.
For your fastening needs, consider the Hex Bolt: Partial Threaded DIN 931 for a solution that combines strength, precision, and longevity.