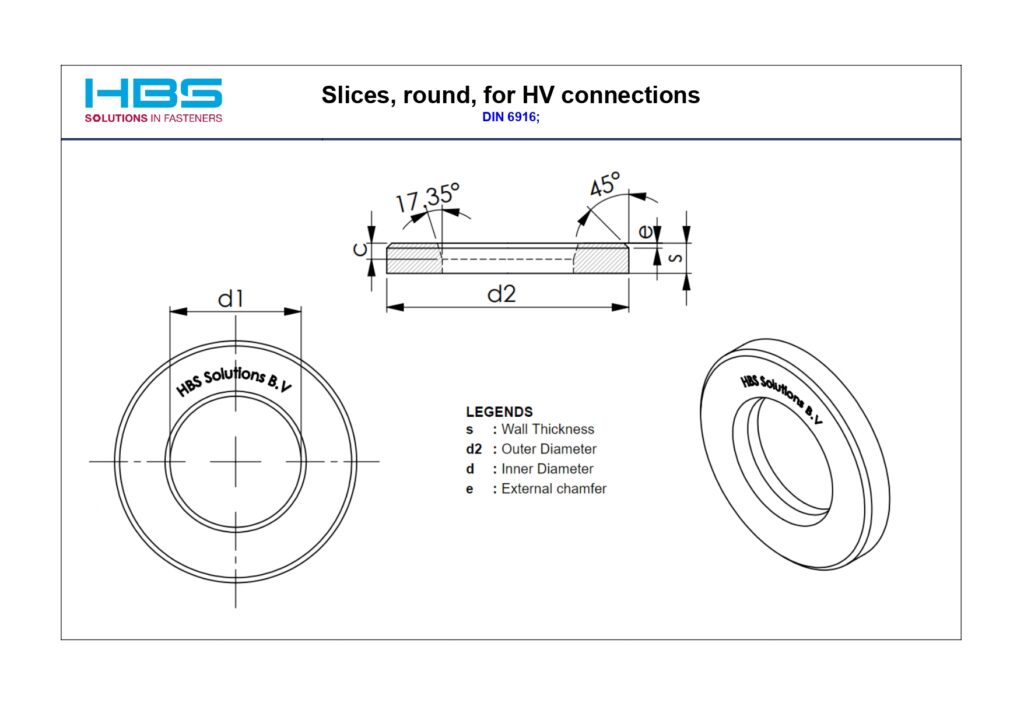
Structural Washer
Technical Specification:
- Structural Washers
- DIN 6916
- Diameter: Metric or Inch
Possible materials:
- ISO: 8.8., 10.9, 12.9
- ISO: A2, A4
- ANSI/ASME: A193-B7, A320-L7, A307
- ANSI/ASME: A193-B8(M) Cl.1 & Cl.2
- DIN Werkstoff: 42CrMo4, 25CrMo4
Possible coatings:
- Carbon steel: Hot-dip Galvanizing, Geomet-500, Zinc, Zinc-Nickel, PTFE/Xylan, TAKECOAT-1000
- Stainless steel: PTFE/Xylan, TAKECOAT-1000
Applications:
- Structural
- Machinery equipment
- Automotive
- Aerospace
Elevating Structural Integrity: DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer
DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer emerges as a cornerstone, fortifying connections and enhancing load distribution. Renowned for its robust construction and superior performance, this washer plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and longevity of structural assemblies. Let’s explore the characteristics, applications, and key distinctions of DIN 6916, highlighting how it sets itself apart from DIN 125 and DIN 127 in delivering unparalleled structural support.
Characteristics of DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer:
DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer is characterized by its larger outer diameter (OD), increased thickness, and hardened steel construction, distinguishing it from conventional washers. These washers are specifically designed to withstand high loads and provide enhanced support in structural applications, where reliability and durability are critical. The larger size and thicker profile of DIN 6916 washers ensure optimal load distribution and resistance to deformation under extreme conditions.Applications and Versatility:
DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer finds widespread application in structural and heavy-duty assemblies, where superior load-bearing capacity and stability are essential. Some common applications include:- Construction and Engineering Projects: In construction projects, bridges, buildings, and infrastructure, DIN 6916 washers reinforce connections in structural elements such as beams, columns, and trusses. Their high-strength properties and increased bearing surface area provide reliable support and stability, ensuring structural integrity and safety.
- Heavy Machinery and Equipment: DIN 6916 washers are used in heavy machinery and equipment, including mining machinery, cranes, and industrial plants, where they secure bolts and nuts in critical components subjected to heavy loads and dynamic forces. Their ability to withstand extreme pressures and resist deformation makes them indispensable for maintaining operational reliability and safety.
- High-Tension Bolting Applications: In applications requiring high-tension bolting, such as offshore structures, power generation facilities, and petrochemical plants, DIN 6916 washers provide essential support and reinforcement. Their high-strength construction and superior load-bearing capacity ensure consistent performance under demanding conditions, reducing the risk of bolt fatigue and failure.
Key Distinctions from DIN 125 and DIN 127:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: Unlike DIN 125 and DIN 127, which are designed for general-purpose applications, DIN 6916 High Strength Structural Washer is specifically engineered to withstand high loads and provide superior support in structural assemblies. Its larger size and thicker profile ensure optimal load distribution and resistance to deformation, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Material and Hardness: DIN 6916 washers are manufactured from hardened steel to withstand extreme pressures and resist deformation under heavy loads. In contrast, DIN 125 and DIN 127 washers may be made from softer materials and are not specifically hardened for structural applications.
- Application Focus: While DIN 125 and DIN 127 washers are suitable for a wide range of fastening applications, DIN 6916 washers are designed specifically for structural and heavy-duty assemblies where reliability, durability, and load-bearing capacity are paramount. Their larger size and thicker profile make them well-suited for high-stress environments and critical structural connections.